

This process yields a much lesser dispersal of matter, since the molecules will occupy a much lesser volume after the gas-to-liquid transition. (b) Condensation is the conversion of a gas (relatively low density) to a liquid (much greater density).

This process yields a much greater dispersal of matter, since the molecules will occupy a much greater volume after the solid-to-gas transition. (a) Sublimation is the conversion of a solid (relatively high density) to a gas (much lesser density). (credit a: modification of work by Jenny Downing credit b: modification of work by “Fuzzy Gerdes”/Flickr credit c: modification of work by Paul A. Uranium-238 is the most abundant isotope of uranium, and its decay occurs much more slowly, exhibiting a half-life of more than four billion years (Figure 9.2.1). Technetium-99m is a popular radioisotope for medical imaging studies that undergoes relatively rapid decay and exhibits a half-life of about six hours. All the decay processes occur spontaneously, but the rates at which different isotopes decay vary widely. Radioactive decay is by definition a spontaneous process in which the nuclei of unstable isotopes emit radiation as they are converted to more stable nuclei. To illustrate this concept, consider the decay of radioactive isotopes, a topic more thoroughly treated in the chapter on nuclear chemistry. A spontaneous change may be so rapid that it is essentially instantaneous or so slow that it cannot be observed over any practical period of time. The spontaneity of a process is not correlated to the speed of the process. At room temperature and typical atmospheric pressure, for example, ice will spontaneously melt, but water will not spontaneously freeze. A process that is spontaneous in one direction under a particular set of conditions is nonspontaneous in the reverse direction.
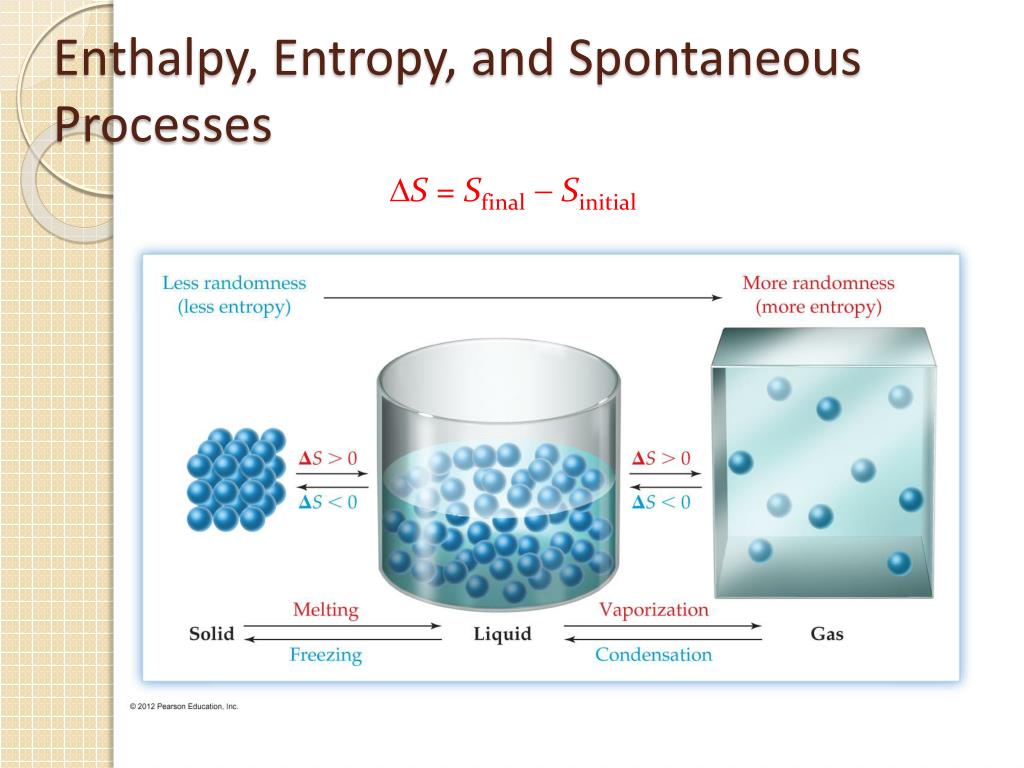
A nonspontaneous process, on the other hand, will not take place unless it is “driven” by the continual input of energy from an external source. A spontaneous process is one that occurs naturally under certain conditions. Iron exposed to the earth’s atmosphere will corrode, but rust is not converted to iron without intentional chemical treatment. Water will naturally flow downhill, but uphill flow requires outside intervention such as the use of a pump. Processes have a natural tendency to occur in one direction under a given set of conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
